| The Mystery of Sleep | The Fascinating World of Dreams | -Fascinating Facts
# An In-Depth Exploration:
Sleep is one of life’s greatest mysteries. Despite its fundamental role in our health and well-being, scientists still do not fully understand why we sleep or what happens during those hours of slumber. This article delves into the complexities of sleep, exploring its stages, significance, and the many unanswered questions surrounding it.
# The Importance of Sleep
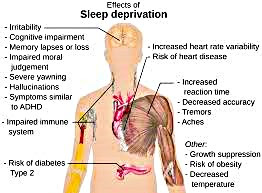
Sleep is essential for various biological functions. It supports physical health, cognitive performance, and emotional regulation. Studies have shown that adequate sleep boosts immune function, enhances memory, and improves problem-solving abilities. Conversely, sleep deprivation can lead to a host of issues, including impaired judgment, increased stress levels, and heightened susceptibility to chronic illnesses like obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
# The Stages of Sleep
Sleep is not a uniform state but consists of distinct stages that cycle throughout the night. These stages are broadly categorized into two types: Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep and Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep.
1. **NREM Sleep**: This stage is further divided into three sub-stages:
- **Stage 1**: The lightest sleep, lasting a few minutes. This is the transition from wakefulness to sleep and involves drowsiness and muscle relaxation.
- **Stage 2**: A deeper sleep, where heart rate slows and body temperature decreases. It accounts for about 50% of total sleep.
- **Stage 3**: Also known as slow-wave sleep (SWS), this is the deepest and most restorative stage. It is crucial for physical recovery, growth, and immune function.
2. **REM Sleep**: This stage occurs after about 90 minutes of sleep and is characterized by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and vivid dreaming. REM sleep is essential for cognitive functions such as memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and learning.
These stages cycle multiple times throughout a typical night, with each cycle lasting about 90 minutes. The balance between NREM and REM sleep is vital for overall health.
# Theories of Why We Sleep
Several theories attempt to explain why we sleep, each highlighting different aspects of its significance:
1. **Restoration Theory**: This theory posits that sleep serves a restorative function. During sleep, the body undergoes repair processes, such as muscle growth, tissue repair, and the release of growth hormones. The brain also detoxifies, clearing out waste products accumulated during wakefulness.
2. **Energy Conservation Theory**: This suggests that sleep evolved as a means to conserve energy. By reducing metabolic demand during periods of inactivity, organisms can save energy and increase survival chances.
3. **Brain Plasticity Theory**: This perspective emphasizes sleep’s role in brain function and plasticity. Sleep enhances synaptic connections, supporting learning and memory consolidation. This theory is supported by the fact that sleep deprivation impairs cognitive function and memory.
4. **Evolutionary Theory**: Some researchers propose that sleep has an evolutionary purpose, providing safety during vulnerable periods (such as night). This theory posits that sleep patterns have evolved to match environmental cues, such as darkness.
# The Role of Circadian Rhythms
Sleep is closely regulated by circadian rhythms—internal biological clocks that dictate the timing of sleep-wake cycles over a 24-hour period. The primary regulator of circadian rhythms is the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in the hypothalamus, which responds to light cues. Disruptions in these rhythms, such as those caused by shift work or jet lag, can significantly impact sleep quality and overall health.
# Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders are prevalent and can drastically affect individuals' quality of life. Some common disorders include:
1. **Insomnia**: Difficulty falling or staying asleep can be acute (short-term) or chronic. It may result from stress, anxiety, or medical conditions.
2. **Sleep Apnea**: A serious condition characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. It often leads to fragmented sleep and daytime fatigue.
3. **Narcolepsy**: A neurological disorder that affects the brain's ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles, leading to excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks.
4. **Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)**: An uncontrollable urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations, which can disrupt sleep.
Understanding these disorders is crucial for improving sleep quality and overall health.
# The Fascinating World of Dreams
Dreaming occurs primarily during REM sleep and remains one of the most intriguing aspects of sleep. While the purpose of dreaming is still not fully understood, several theories exist:
1. **Psychological Processing**: Dreams may serve to process emotions and experiences from waking life, helping individuals work through unresolved conflicts or stressors.
2. **Memory Consolidation**: Some researchers believe that dreams play a role in memory formation, helping to organize and integrate memories from the day.
3. **Problem-Solving**: Dreams may facilitate creative thinking and problem-solving, allowing the brain to make new connections and insights.
Despite these theories, the precise function of dreams continues to elude definitive explanation.
# Cultural Perspectives on Sleep
Sleep has been perceived differently across cultures and throughout history. In many societies, sleep rituals, bedtime stories, and communal sleeping practices are commonplace. The significance of dreams also varies, with some cultures viewing them as prophetic or spiritually meaningful.
# The Future of Sleep Research
As research into sleep continues to evolve, new technologies, such as polysomnography and functional MRI, are enhancing our understanding of sleep processes. The exploration of sleep's genetic and molecular underpinnings may one day unlock further mysteries.
Additionally, the rise of sleep health awareness has prompted a focus on improving sleep hygiene practices, such as establishing consistent sleep schedules, creating comfortable sleep environments, and minimizing exposure to screens before bedtime.
# Conclusion
Sleep remains a complex and fascinating area of study. While we understand its critical importance for physical health, cognitive function, and emotional well-being, many questions remain unanswered. As researchers delve deeper into the mysteries of sleep, we may uncover new insights that not only enhance our understanding of this essential human experience but also improve our overall quality of life. Understanding sleep better can lead to improved health outcomes, greater productivity, and a deeper appreciation for this enigmatic aspect of our existence.













Post Comment
No comments
Hello! Guys, If you have any doubts please comment